Demystifying Embedded Finance: Everything You Need to Know
Embedded finance is changing the face of e-commerce, allowing businesses to grow by providing customers with smooth and safe payment experiences.
Earlier, online transactions usually posed the risk of payment fraud since clients had to provide sensitive account or card details directly on websites during purchases.
However, with the arrival of embedded finance platforms such as PayPal and Stripe, customers gained trust and confidence in online transactions.
In 2022, the United States led the way in embedded financial revenue, with over $26.5 billion, closely followed by the United Kingdom, which had more than four billion US dollars.
This trend highlights the expanding use and relevance of embedded finance in current business, as companies explore new methods to improve customer happiness and generate revenue growth.
What is embedded finance?
Embedded finance is the integration of financial services into non-financial systems, resulting in frictionless transactions and improved user experiences. Essentially, it allows businesses to integrate financial capabilities directly into their products or services, removing the need for clients to contact outside financial institutions.
This approach is transforming several industries, including e-commerce, healthcare, travel, and hospitality. For example, an e-commerce platform may include payment processing and lending services, allowing clients to purchase and obtain credit without leaving the site.
Similarly, a healthcare app may provide insurance coverage and payment alternatives, making the billing process easier for patients. Overall, integrated finance improves ease, accessibility, and efficiency, hence stimulating innovation and altering established business structures.
What is embedded finance examples?
Embedded finance examples span several sectors and use scenarios in which financial services are smoothly incorporated into non-financial systems.
For example, in e-commerce, payment gateways such as PayPal or Stripe are integrated into online storefronts, allowing for safe transactions without diverting customers to other payment pages.
Similarly, in the travel business, booking platforms may include travel insurance and currency conversion services, providing passengers with ease and peace of mind.
Furthermore, in the healthcare industry, telemedicine systems may include invoicing and insurance processing features, making the payment process easier for patients.
These examples show how integrated finance improves user experiences and facilitates transactions across sectors.
What is the meaning of embedded banking?
Embedded banking is the integration of banking services into non-banking platforms or apps, allowing customers to access financial services easily as part of their daily activities.
For example, integrated banking may be found in e-commerce platforms that provide payment processing services immediately inside the checkout process, removing the need for consumers to visit a separate banking website or application to complete transactions.
Comparably, integrated banking can take the form of budgeting or financial management apps that provide users access to their bank accounts and allow them to make transactions without leaving the app.
This connection simplifies the user experience and increases access to banking services, eventually enhancing financial management for both people and enterprises.
Is embedded finance the future?
Embedded finance, or the integration of financial services into non-financial platforms, represents the future of banking and finance. With the rising digitalization of sectors, embedded finance provides simple, smooth, and personalized financial solutions integrated into routine activities.
Numerous companies, ranging from fintech startups to established banks, are using integrated finance to improve the customer experience, promote innovation, and open up new income sources.
Examples include ride-sharing applications like Ola that accept payments, e-commerce platforms that provide loans at checkout, and software platforms that integrate invoicing and payment features.
As technology advances and customer expectations shift, embedded finance will play a critical role in determining the future of banking and financial services, providing consumers globally with increased accessibility, efficiency, and customization.
What is the difference between open banking and embedded finance?
Open banking and embedded finance are two distinct concepts that revolutionize the financial industry, yet they serve different purposes and functions.
Open banking refers to the practice of banks and financial institutions allowing third-party developers to access their customer data through APIs. This enables fintech companies to create innovative financial products and services, such as budgeting apps, investment platforms, and payment solutions, by leveraging customer data from multiple banks.
On the other hand, embedded finance involves the integration of financial services directly into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce websites, ride-sharing apps, and software platforms.
Unlike open banking, which focuses on data sharing, EF focuses on offering financial services seamlessly within existing customer experiences.
For example, an e-commerce platform may offer instant loans or installment payments at checkout, while a ride-sharing app may provide insurance options or digital wallets for payment.
While both open banking and embedded finance promote innovation and collaboration within the financial sector, open banking focuses on data sharing through APIs, while embedded finance emphasizes the integration of financial services into non-financial platforms to enhance user experience and accessibility.
What are the key drivers of embedded finance?
Embedded finance is being driven by several key factors that are reshaping the financial landscape and driving innovation in the industry.
1# Consumer Expectations
With the rise of digital technology, consumers expect seamless and convenient financial services integrated into their everyday activities. EF meets this demand by offering financial services within existing digital platforms, such as e-commerce websites, social media platforms, and mobile apps.
2# Technology Advancements
Rapid advancements in technology, such as APIs, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, have made it easier to integrate financial services into various digital platforms. This enables businesses to offer personalized and efficient financial solutions to their customers.
3# Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes, such as open banking initiatives, PSD2 (Revised Payment Service Directive), and other fintech-friendly regulations, are encouraging collaboration and innovation within the financial sector. These regulations promote data sharing and interoperability, making it easier for businesses to integrate financial services into their platforms.
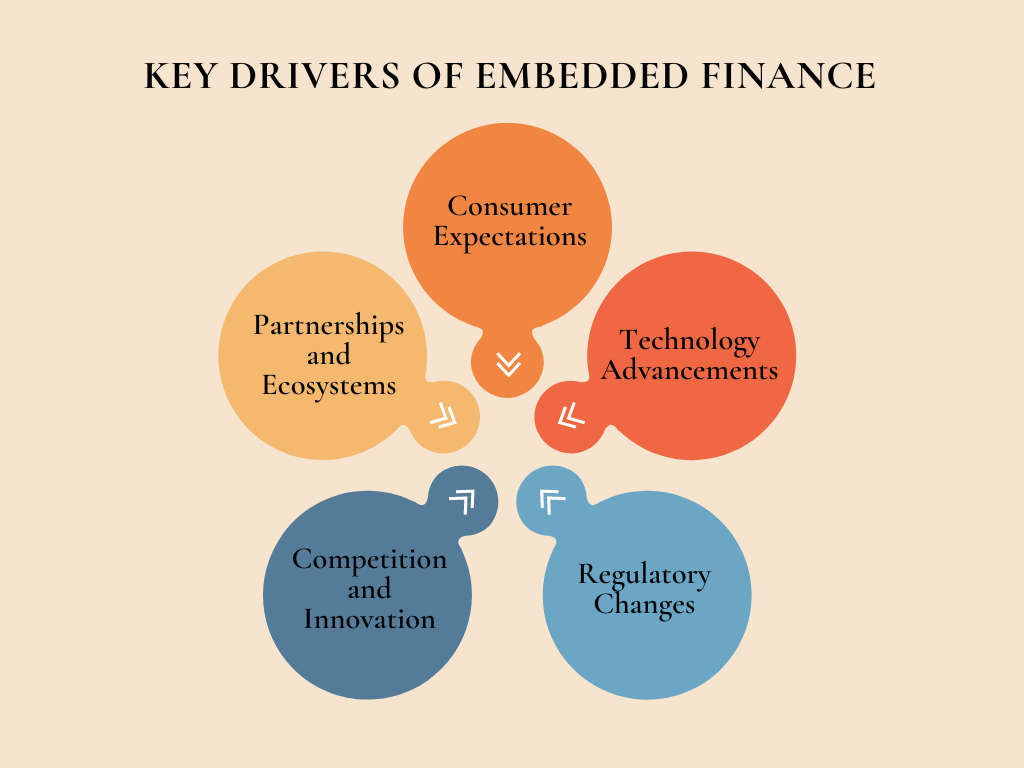
4# Competition and Innovation
The increasing competition in the financial services industry is driving traditional banks and fintech companies to innovate and differentiate their offerings. Embedded finance provides an opportunity for businesses to create unique value propositions by offering tailored financial services that meet the specific needs of their customers.
5# Partnerships and Ecosystems
Collaboration between traditional financial institutions, fintech startups, and non-financial companies is fueling the growth of embedded finance. By partnering with fintech companies, businesses can leverage their expertise and technology to offer innovative financial solutions to their customers.
The key drivers of EF include evolving consumer expectations, technological advancements, regulatory changes, competition and innovation, partnerships, and ecosystems. These factors are driving the adoption of embedded finance and transforming the way financial services are delivered and consumed.
What is the role and impact of embedded finance?
It plays an important role in reshaping the traditional financial landscape and revolutionizing the way people access and use financial services. With embedded finance, financial products and services are seamlessly integrated into everyday experiences and platforms, such as e-commerce websites, mobile apps, and software applications.
The impact of embedded finance is significant and far-reaching. Firstly, it democratizes access to financial services by making them more convenient and accessible to a wider audience.
For example, embedded finance allows users to access loans, insurance, and investment products directly from their favorite apps or platforms, eliminating the need to visit physical bank branches.
Moreover, it drives innovation and fosters collaboration between traditional financial institutions and non-financial businesses. By integrating financial services into their offerings, non-financial companies can enhance customer engagement, loyalty, and satisfaction.
For instance, a ride-sharing app offering instant insurance coverage or a retail platform providing buy-now-pay-later options at checkout.
Overall, embedded finance empowers businesses to create new revenue streams, enhance customer experiences, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital economy. Its role will continue to expand as more industries embrace the integration of financial services into their products and services.
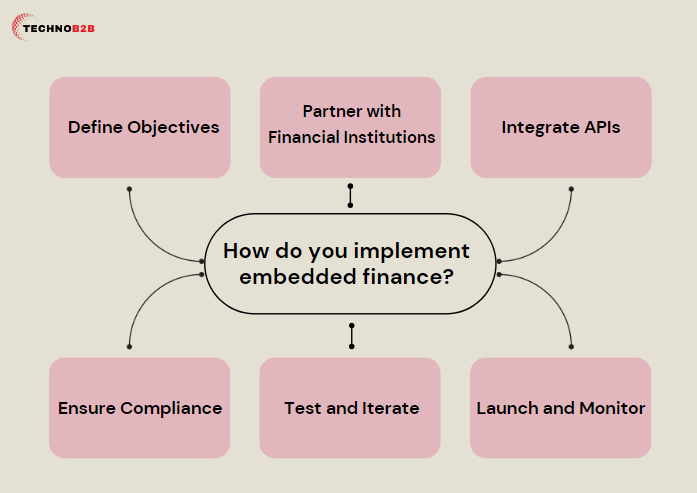
How do you implement embedded finance?
Implementing embedded finance involves several key steps to seamlessly integrate financial products and services into existing platforms or applications. Here’s how to do it:
1# Define Objectives
Begin by identifying the specific financial services you want to embed and the goals you aim to achieve, such as enhancing the user experience or generating additional revenue.
2# Partner with Financial Institutions
Collaborate with banks, fintech companies, or financial institutions to access the necessary financial products and APIs required for embedding finance.
3# Integrate APIs
Utilize Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) provided by financial partners to integrate financial functionalities, such as payments, loans, or insurance, into your platform or application.
4# Ensure Compliance
Adhere to regulatory requirements and compliance standards, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, to ensure the legality and security of embedded financial services.
5# Test and Iterate
Conduct thorough testing of the embedded finance features to ensure functionality, security, and user experience. Gather feedback from users and iterate based on their suggestions and preferences.
6# Launch and Monitor
Once implemented, launch the embedded finance features and closely monitor performance metrics, such as adoption rates, transaction volumes, and user feedback, to assess effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments.
By following these steps, businesses can successfully implement embedded finance solutions to enhance their offerings and provide added value to their customers.
FAQs
1. What is embedded finance?
Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial services, like payments, loans, or investments, directly into non-financial platforms like ride-sharing apps, e-commerce websites, or even social media. This means you can access and utilize these financial services without leaving the platform you’re already using.
2. How does embedded finance work?
Embedded finance relies on technology, specifically Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which act as bridges between different platforms. These APIs allow the non-financial platform to securely connect with a financial institution or service provider, enabling seamless integration and data exchange.
3. What are some examples of embedded finance?
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL): E-commerce platforms offering installment payment options at checkout.
- Ride-sharing apps: Paying for your rides directly within the app using a linked payment method.
- Neobanks: Digital banks providing investment options within their banking app.
- E-commerce platforms: Offering insurance coverage for purchases directly on the platform.
4. What are the benefits of embedded finance?
- Convenience: Accessing financial services readily within familiar platforms.
- Improved user experience: Seamless integration avoids the need to switch between apps or websites.
- Increased access: Makes financial services more accessible to a wider audience, especially those who might not have access to traditional banking channels.
- Tailored offerings: Platforms can personalize financial offerings based on user data and behavior.
5. What are some potential challenges of embedded finance?
- Data security and privacy: Ensuring secure data sharing between platforms and financial institutions is crucial.
- Regulatory considerations: Navigating regulations that apply to both financial services and the non-financial platform.
- Consumer protection: Ensuring responsible lending practices and transparent service terms for users.




